Đề thi IELTS Writing Task 1 ngày 22/02/2025 kèm bài mẫu band 8.5+
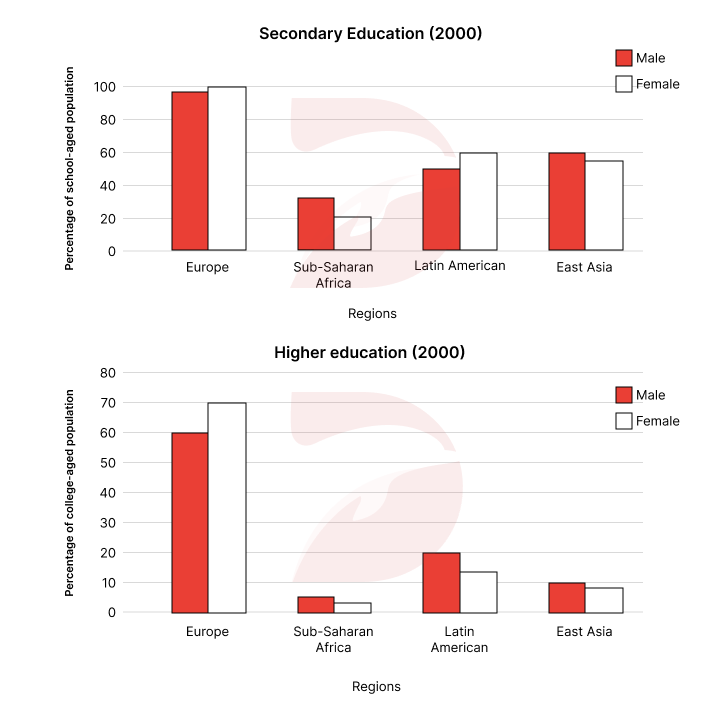
Đề thi IELTS Writing Task 1 ngày 22/02/2025 dạng Bar chart: The first chart below shows the percentage of school-aged girls and boys who were at secondary school in four regions of the world in 2000. The second chart shows the percentages of college-aged men and women in higher education in the same year.
🚀 Đề bài
😵 Dàn ý
DOL sẽ miêu tả biểu đồ với 1 câu mở bài (Intro), 1 đoạn miêu tả tổng quát (Overview), và 2 đoạn thân bài miêu tả chi tiết (Detailed Description)
Mở bài: DOL sẽ paraphrase đề bài để giới thiệu lại đề bài cho người chấm
Miêu tả tổng quát: DOL sẽ chỉ ra các đặc điểm quan trọng, nổi bật nhất trong biểu đồ.
Thân bài:
Body 1: DOL trình bày tỷ lệ nam và nữ sinh trung học ở bốn khu vực năm 2000.
Body 2: DOL trình bày tỷ lệ nam và nữ sinh đại học ở bốn khu vực năm 2000.
- Europe: females > males (100% & 98%).
- Latin America: females (60%) > males (50%).
- East Asia: 60% males ~ 2x Sub-Saharan Africa.
- Female rates: 55% (East Asia), 20% (Sub-Saharan Africa).
- Europe: highest - females (70%) > males (60%).
- Latin America: males (20%) > females (15%).
- East Asia: males (10%) > females (9%).
- Sub-Saharan Africa: most significant disparity - males (5%), females (3%).
📝 Bài mẫu
The bar charts provide information on the proportion of school-aged and college-aged students who were able to pursue secondary and higher education, categorized according to gender in four regions namely Europe, Sub-Saharan Africa, Latin America and East Asia in 2000.
Overall, there were more female students than male students in secondary schools in Europe and Latin America, while the opposite trend was observed in the remaining regions. Regarding higher education, all regions
In terms of secondary education, the percentage of school-aged females was higher than that of males in Europe, though the gender gap was
As for higher education, Europe had the highest attendance rates, with females
(293 words)
📚 Vocabulary
✨ Bài tập Exercise
Mình cùng làm 2 bài tập sau đây để ôn lại các từ vựng và cấu trúc đã được dùng trong bài IELTS Writing Sample Task 1 nhé!
Exercise 1: Điền từ / cụm từ phù hợp để hoàn thành câu sau.
1 Nhà khoa học ghi nhận sự thay đổi nhiệt độ mỗi giờ.
-> The scientist
2 Tỷ lệ tham dự của trường được cải thiện sau khi áp dụng các chính sách mới.
-> The school's
3 Thiệt hại đối với chiếc xe là tối thiểu sau vụ tai nạn.
-> The damage to the car was
4 Doanh số bán hàng trực tuyến chiếm gần một nửa doanh thu của công ty.
-> Online sales
Exercise 2: Tìm những từ / cụm từ tiếng Anh phù hợp với những từ / cụm từ sau.
nhiều hơn
khoảng
vượt qua
sự chênh lệch đáng kể
💡 Lời kết
Tới đây là hết rồi 😍 Sau sample “The first chart below shows the percentage of school-aged girls and boys who were at secondary school in four regions of the world in 2000. The second chart shows the percentages of college-aged men and women in higher education in the same year.", DOL mong các bạn không chỉ nắm được cách trả lời cho dạng bài Bar chart, mà còn học được những từ vựng và cấu trúc hay để miêu tả các biểu đồ tương tự nhé.
🤩 Mình cùng nhau học lại những cấu trúc hay đươc dùng trong bài nhé!
1. Cách dùng "that" thay thế cụm noun để tránh lặp từ
Ví dụ: In terms of secondary education, the percentage of school-aged females was higher than that of males in Europe.
Phân tích:
📌 Câu được viết đầy đủ cả 2 cụm noun sẽ là:
In terms of secondary education, the percentage of school-aged females was higher than the percentage of school-aged males in Europe.
=> "the percentage" đã bị lặp lại.
=> Thay thế "the percentage" bằng "that" để tránh lặp từ.
=> Câu viết lại sẽ là: In terms of secondary education, the percentage of school-aged females was higher than that of school-aged males in Europe. (that = the percentage)
📌 Trong "that of school-aged males", cụm "school-aged" có thể được hiểu ngầm từ ngữ cảnh.
Do đó, mình có thể rút gọn thành:
👉 In terms of secondary education, the percentage of school-aged females was higher than that of males in Europe.
📌 Tóm tắt:
Higher than the percentage of school-aged males → higher than that of school-aged males → higher than that of males
2. Cấu trúc so sánh
📌 So sánh số lượng
Cấu trúc: SV + more + noun + than + O
Ví dụ: There were more female students than male students in secondary schools in Europe and Latin America.
📌 So sánh hơn với Adjective ngắn
Cấu trúc: SV + Adj_er + than + Noun
Ví dụ: The percentage of school-aged females was higher than that of males in Europe.
📌 So sánh nhất với Adjective ngắn
Cấu trúc: SV + the + Adj_est + Noun
Ví dụ: Europe had the highest proportion of students with access to both levels of education across genders.
📌 So sánh nhất với Adjective dài
Cấu trúc: SV + the most + Adj + Noun
Ví dụ: Lastly, Sub-Saharan Africa showed the most significant disparity in access to higher education.
3. Cấu trúc tương phản
📌 SV, while SV
Ví dụ: There were more female students than male students in secondary schools in Europe and Latin America, while the opposite trend was observed in the remaining regions.
📌 SV, though SV
Ví dụ: The percentage of school-aged females was higher than that of males in Europe, though the gap was minimal, with males accounting for around 98% and females reaching nearly 100%.
📌 SV. In contrast, SV
Ví dụ: In Latin America, females also outnumbered males, with roughly 60% of females and 50% of males attending school. In contrast, Sub-Saharan Africa and East Asia had higher male attendance rates compared to females, with 60% of boys attending school in East Asia.
Nếu có thời gian thì nhớ làm phần bài tập và tự mình viết một bài khác nha vì 'Practice makes perfect' mà nhỉ? DOL chúc các bạn học tốt! 


